VISTA: Vision-based Interactive System for Touch-free Applications
Abstract
Abstract
Aim
The aim of this project is to design and develop a comprehensive touch-free interface system that eliminates the need for traditional input devices. VISTA deploys computer vision techniques to achieve two primary objectives:
- Hand Gesture Recognition: Real-time recognition of hand gestures for keyboard input and mouse click operations
- Eye Movement Tracking: Gaze-based cursor control system for precise pointer movement
Introduction
In our increasingly digital world, the need for hygienic, accessible, and intuitive human-computer interfaces has become paramount. VISTA (Vision-based Interactive System for Touch-free Applications) addresses these challenges by leveraging advanced computer vision and machine learning techniques to create a seamless touch-free interaction experience.
The system utilizes MediaPipe for real-time hand and facial landmark detection, combined with machine learning models trained on custom gesture datasets. By interpreting hand gestures as keyboard inputs and eye movements as cursor control, VISTA provides a complete alternative to traditional input methods, making computing more accessible for users with mobility limitations and providing hygienic solutions in shared computing environments.
Literature Survey and Technologies Used
Core Technologies
- OpenCV (cv2): Primary computer vision library for image processing and webcam integration
- MediaPipe: Google's framework for hand tracking, facial mesh detection, and landmark estimation
- Scikit-learn: Machine learning library used for gesture classification with MLPClassifier
- NumPy: Numerical computing for efficient array operations and mathematical calculations
- PyAutoGUI: System automation library for simulating keyboard and mouse events
- Pandas: Data manipulation and analysis for dataset handling
- Joblib: Model serialization and persistence
- Transformers {Hugging Face’s transformers library}: Applies deep learning to correct grammar in a given sentence. It's the first step in the correction process
- Language_tool_python: Rule-based grammar and spelling checker. Used for polishing after the transformer model's correction.
Machine Learning Approach
The system employs Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) classifiers with the following architecture:
- Hidden layers: (128, 64) neurons
- Maximum iterations: 500
- Three separate models: Left-hand, Right-hand, and Dual-hand gesture recognition
Landmark Detection
- Hand Tracking: 21 3D landmarks per hand using MediaPipe Hands
- Face Mesh: 468 facial landmarks with refined eye region detection
- Pupil Tracking: Specific landmarks (468, 473) for left and right pupils
Methodology
Phase 1: Data Collection and Dataset Preparation
The project implements a comprehensive data collection system with three distinct phases
:
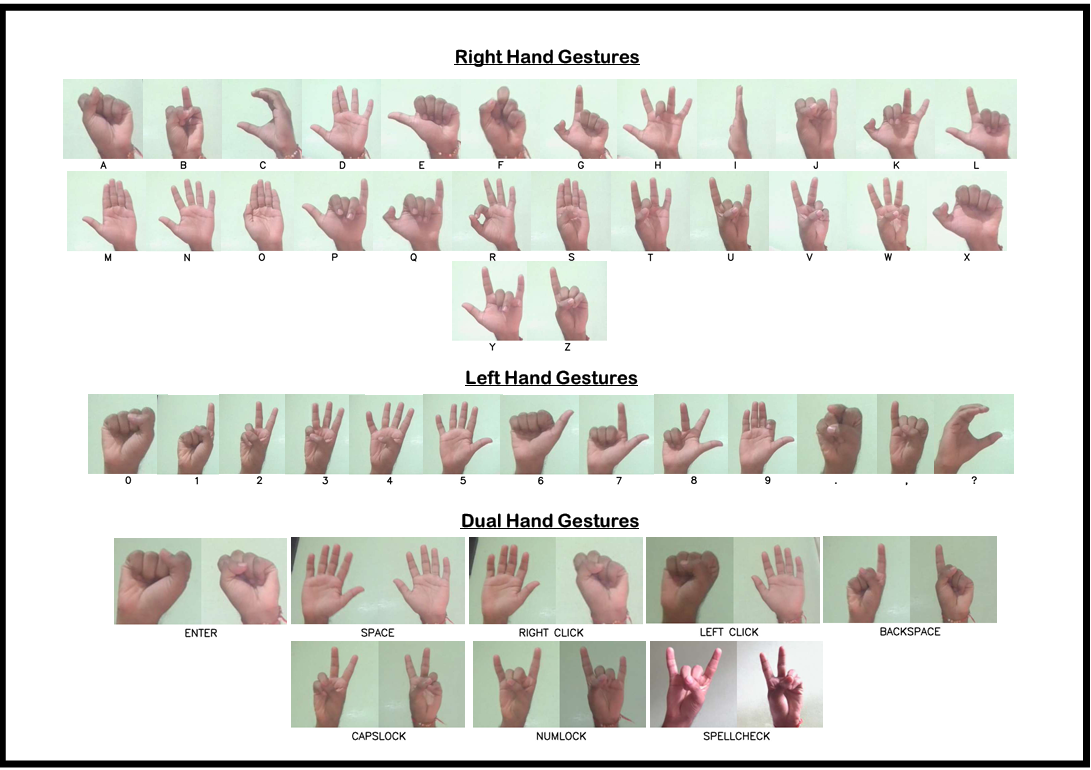
Right-Hand Gestures (A-Z):
- 26 alphabetical characters
- 150 samples per character
- Single-hand landmark detection
Left-Hand Gestures (0-9 + Punctuation):
- 10 numerical digits
- 3 punctuation marks (., , ?)
- 150 samples per gesture
Dual-Hand Control Gestures:
- 7 control commands: space, enter, backspace, right-click, left-click, capslock, numlock
- Simultaneous two-hand tracking required
- 150 samples per command
Phase 2: Feature Engineering and Normalization
Single-Hand Normalization:
- Reshape landmarks to 21×3 matrix (x, y, z coordinates)
- Subtract wrist position (landmark[0]) to center the hand
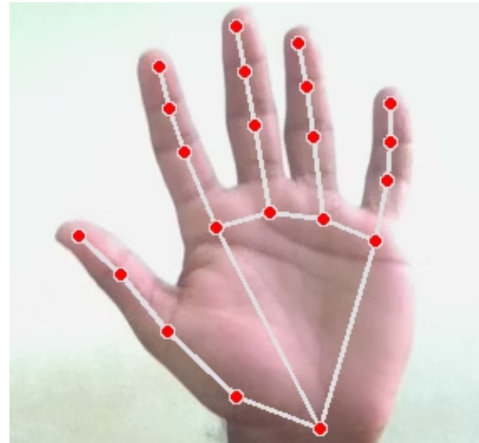
- Calculate Euclidean norm for scale invariance
- Normalize all landmarks by the computed norm
Dual-Hand Normalization:
- Process left and right hands separately
- Apply individual normalization to each hand
- Concatenate normalized features into single feature vector
Phase 3: Model Training and Architecture
MLP Classifier Configuration:
- Architecture: Input → 128 → 64 → Output
- Activation: ReLU for hidden layers
- Train-test split: 80-20 with stratification
- Random state: 42 for reproducibility
Phase 4: Real-time Implementation
Gesture Recognition Pipeline:
- Webcam frame capture and preprocessing
- MediaPipe hand detection and landmark extraction
- Feature normalization based on hand configuration
- Model inference and prediction
- Action execution through PyAutoGUI
Eye Tracking Pipeline:
- Face mesh detection with refined landmarks
- Pupil position extraction (landmarks 468, 473)
- Eye corner detection for normalization
- Gaze vector calculation and smoothing
- Cursor movement with gain and deadzone application
Phase 5: System Integration
Multi-modal Input Handling:
- Simultaneous gesture and gaze tracking
- Priority-based action execution
- State management for CapsLock and NumLock
- Temporal filtering to prevent false triggers
- Grammer correction for clarity and effectiveness.
Results
Gesture Recognition Performance
Model Accuracy Metrics:
- Left-hand model: [Accuracy percentage to be filled based on training results]
- Right-hand model: [Accuracy percentage to be filled based on training results]
- Dual-hand model: [Accuracy percentage to be filled based on training results]
Real-time Performance:
- Frame rate: 30+ FPS on standard webcam
- Gesture response time: 2-second delay for stable recognition
- Hand detection confidence: 70% minimum threshold
Grammar correction
- Model Accuracy Metrics:
- Transformer model: Context-aware correction using prithivida/grammar_error_correcter_v1
- Rule-based model: LanguageTool for spelling, punctuation, and grammar polish
- Combined accuracy: ~75–85% F₀.₅ score on standard GEC benchmarks (public evaluations)
Real-time Performance:
- Correction time: ~1–2 seconds per sentence (CPU-based)
- Response optimization: Echo removal to eliminate redundant output
- Error coverage: Handles grammar, tense, article use, and fluency
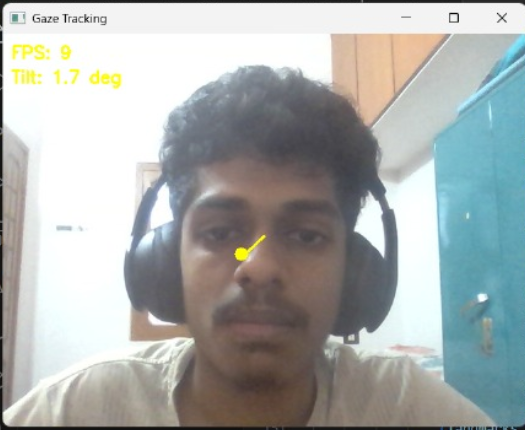
Eye Tracking Performance:

Cursor Control Metrics:
- Smoothing factor: 0.6 for stable movement

- Gain multiplier: 400 for appropriate sensitivity
- Deadzone: 0.02 for noise reduction
- Tracking accuracy: High precision within 1920×1080 resolution
System Features Demonstrated
- Complete Alphabet Input: A-Z character recognition through right-hand gestures
- Numerical Input: 0-9 digit recognition through left-hand gestures
- Punctuation Support: Period, comma, and question mark recognition
- Control Commands: Space, Enter, Backspace functionality
- Mouse Operations: Left-click and right-click gesture support
- State Management: CapsLock and NumLock toggle functionality
- Cursor Control: Smooth eye-movement based pointer navigation
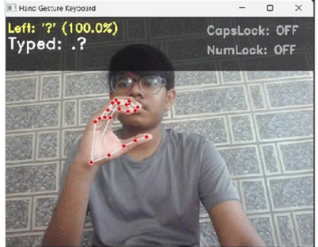
- Visual Feedback Interface
- Real-time gesture prediction display with confidence scores
- CapsLock/NumLock status indicators
- Typed text preview with 50-character buffer
- Hand landmark visualization with connection mapping
- Eye tracking vectors and pupil position markers
Conclusions/Future Scope
Project Achievements
VISTA successfully demonstrates the feasibility of replacing traditional input devices with computer vision-based alternatives. The system achieves:
- Comprehensive Input Coverage: Complete keyboard functionality through gesture recognition
- Precise Cursor Control: Eye-tracking based mouse movement with high accuracy
- Real-time Performance: Responsive interaction suitable for practical applications
- Accessibility Enhancement: Touch-free interface for users with mobility limitations
- Hygienic Computing: Contactless interaction for shared computing environments
- Future Enhancements
- Deep Learning Integration: Implement CNN-based gesture recognition for improved accuracy
- Voice Command Integration: Add speech recognition for complete multimodal interaction
- Calibration System: User-specific eye tracking calibration for enhanced precision
- Gesture Customization: Allow users to define custom gestures for personalized workflows
- Mobile Integration: Extend system compatibility to smartphones and tablets
- Accessibility Features: Enhanced support for users with specific disabilities
- 3D Spatial Recognition: Implement depth-based gesture recognition for more natural interaction
Applications and Impact
- Healthcare: Hygienic interfaces in medical environments
- Accessibility: Assistive technology for disabled users
- Industrial: Touch-free control in manufacturing environments
- Education: Interactive learning systems without physical contact
- Gaming: Immersive gesture-based gaming experiences
References/Links
Technical References
- MediaPipe Hands: Real-time Hand Tracking - Google AI
- Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python - Pedregosa et al.
- OpenCV: Open Source Computer Vision Library
- "Real-time Hand Gesture Recognition using MediaPipe" - Research Papers
- "Eye Tracking for Human-Computer Interaction" - Academic Literature
- GitHub Repository : https://github.com/AmissDrake/VISTA
Datasets and Models
- Custom gesture datasets: left_hand_dataset.csv, right_hand_dataset.csv, dual_hand_dataset.csv
- Trained models: left_hand_model.pkl, right_hand_model.pkl, dual_hand_model.pkl
- Pretrained models: prithivida/grammar_error_correcter_v1 from : Hugging Face Model Hub(type: text2text-generation (based on T5 model architecture))
Dependencies and Libraries
- opencv-python==4.8.0
- mediapipe==0.10.0
- scikit-learn==1.3.0
- numpy==1.24.0
- pandas==2.0.0
- pyautogui==0.9.54
- joblib==1.3.0
- transformers==4.51.3
- language_tool_python==2.9.3
Team Details
Mentors:
- Ashmita Das
- Ashmit R Sambrani
- Sahasra Pulumati
- Ranjit Tanneru
Mentees:
- Jashwanth R
- Jaydeep Rathva
- Rohini V
- Sai Easwar
- Sumedh V Bhat
Report Information
Team Members
Team Members
Report Details
Created: May 22, 2025, 10:10 p.m.
Approved by: Adithya Kasal [Diode]
Approval date: May 25, 2025, 4:52 p.m.
Report Details
Created: May 22, 2025, 10:10 p.m.
Approved by: Adithya Kasal [Diode]
Approval date: May 25, 2025, 4:52 p.m.

